Aculab Cloud Java UAS Overview
Aculab Cloud
Aculab Cloud allows development of voice applications through a cloud-based
media processing and communications platform. Your applications are developed
using high-level languages such as Python, C#, VB, F#, C++ and Java and
run within a
User Application Server (UAS)
that resides on your own platform.
Inbound applications run in response to specific incoming calls to the cloud. Outbound
applications run in response to specific requests to invoke them (e.g. via a web interface).
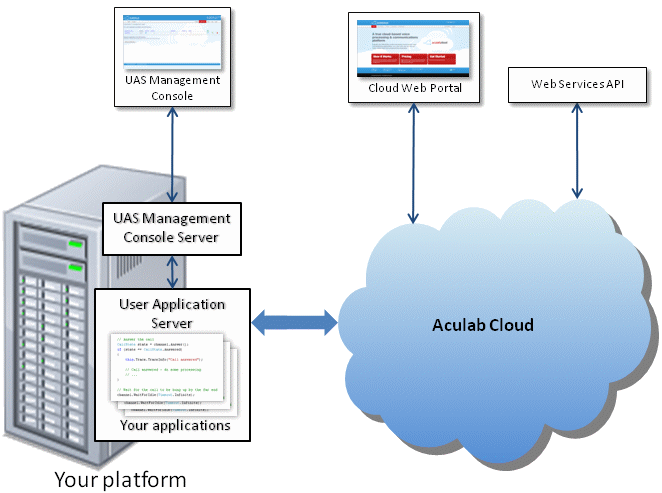
The UAS is configured and monitored via the
UAS Management Console.
Users create their own accounts on the cloud via
cloud.aculab.com. This allows them to configure
how individual applications are invoked, to invoke outbound applications and to manage
their media files on the cloud through a graphical web interface.
A Web Services (WS) API provides a programmatic means of doing the same things.
Language Support
UAS download packages are available that support a variety of programming languages.
The following documentation refers to the Java UAS which provides Java APIs
for writing applications.
A number of sample Java UAS applications are provided with this UAS that illustrate some
typical simple scenarios.
In addition, a few Java samples have been included that illustrate how to use the various Web Service interfaces.
Architecture
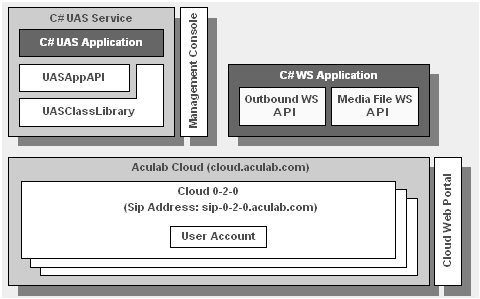
The Java UAS runs applications that use the com.aculab.uasapi library.
These provide call handling, media processing, file handling and diagnostic facilities.
Standalone Web Service applications use the WS API to invoke outbound applications, to monitor their
progress, to manage media files and to manage large conference reservations.
The UAS receives a request from the Aculab Cloud
instructing it to run a selected user application that is currently loaded in the UAS.
User applications typically handle a primary call, either inbound or
outbound, and may make other secondary outbound calls. A call may be connected
or transferred to another call.
A UAS application is invoked by the cloud in response to either an incoming call to
a specific address or to a request to invoke an application that makes an outbound call.
Compatibility:
The Java UAS is compatible with Windows XP/2008/7 and typical Linux distributions.
Pre-requisites:
The Java UAS is built using
JEE 7 and requires a suitable version of this installed and available.
In order to develop UAS applications JDK 1.7 will need to be installed. Otherwise, just JRE 1.7 will suffice.
UAS Management Console
Use the Management Console to manage cloud connections, applications and diagnostic information
on the UAS.
Cloud Configuration
The UAS maintains a list of clouds to which it holds a connection. Following first-time
installation on a platform the UAS needs to be configured with details of the cloud(s)
that are to use it.
See the
Using the UAS section for
instructions on how to add and remove cloud details from the UAS.
Application Management
Applications developers can upload, remove, monitor and diagnose their applications.
See the
Using the UAS section for
instructions on how to manage applications on the UAS.
Writing Telephony Applications
A UAS application is simply a Java class library packaged into a jar file and that uses the uasapi and amsapi,
libraries adhering to a few simple conventions.
The UAS API is based on the Aculab Media System (AMS) Client API which provides powerful media processing and call control
features via a high-level client API. It allows incoming and outgoing telephone calls to be controlled and
connected together or transferred, wav file playback, wav file record, DTMF playback, DTMF detection,
fax sending, fax receiving and conferencing.
See the
Writing Applications section for
guidance on developing applications for the UAS.
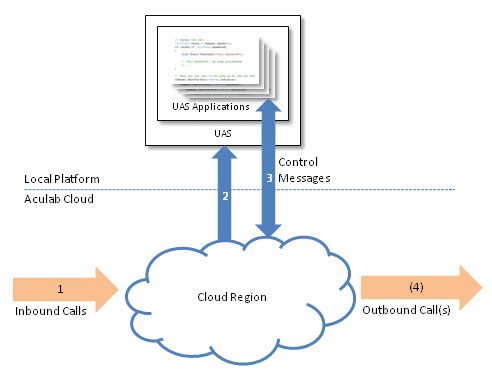
Inbound Applications
The target address of an incoming call
(1) is used to determine which application
is to be executed. A message is sent to the UAS to run an instance of the specified application
(2).
The application is handed an active incoming call and its first task is typically either to answer it or reject
it
(3). Optionally, the application can also make an
additional outbound call
(4).
Inbound Services
An Inbound Service must be registered on the relevant cloud region in order for it to be able to invoke a
particular inbound application in response to an incoming call. Each Inbound Service points to exactly one
application while several Inbound Services can point to the same application.
You can create a new Inbound Service from
Inbound Services
(requires you to be logged in).
Invoking Outbound Applications
While inbound applications are run automatically in response to incoming calls, outbound applications are typically
invoked externally to the cloud, via a standalone program. A sample application is provided
here.
Note that UAS applications can also invoke outbound applications.
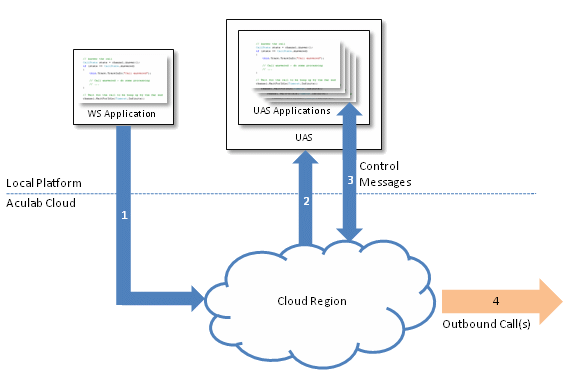
The Aculab Cloud Web Services API can be used to write a
WS Application
that invokes an outbound application on a particular cloud region
(1).
A message is sent to the UAS to run an instance of the specified outbound
application
(2). The outbound application typically then makes an
outbound call
(3,4). As for an inbound application, an outbound application
can usually also make additional outbound calls
(4).
Outbound Services
An Outbound Service must be registered on the relevant cloud region in order for it to be able to invoke a
particular outbound application. Each Outbound Service points to exactly one application while several
Outbound Services can point to the same application.
You can create a new Outbound Service from
Outbound Services
(requires you to be logged in).
Outbound Parameters
The particular cloud region and user's account on which an Outbound Service resides are specified through the WS API.
In addition this API provides an
outboundParameters field that will ultimately
be passed to the outbound application. Typically this contains the destination address of the resultant outbound call.
Media files that applications may play or record reside on the cloud.
Some basic file manipulation methods are available to applications.
In addition, the Web Services API can be used to perform media file management.
See the
Manage Media Files Web Service Sample.




